In Europe, thermal wind generators are being developed, which, in combination with the use of new technologies, are more energy-efficient installations than classic wind turbines.
This is stated in the article on the LowTechMagazine.com profile site. The authors emphasize that mankind has used windmills for two thousand years, but only recently figured out how to use them to produce thermal energy.
In a thermal wind generator, mechanical energy is converted into thermal energy according to the principle that the English physicist Joule first applied in 1840 to measure the mechanical heat equivalent. The heat generator is an insulated water tank in which there is an impeller driven by a wind turbine.
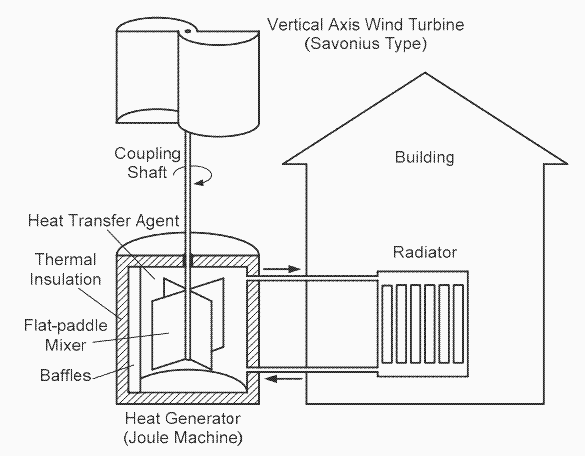
Water heats up due to friction between water molecules. The liquid heated in this way is pumped for heating in the house.
Unlike electric wind generators, in mechanical versions there is no electric generator, transformer, gearbox. They have a lower mass, are simple in design, less complicated to manufacture and install, and are also able to last for a longer time.
The main problem associated with the generation of heat is the inconsistency of wind speed. To solve this problem, thermal wind turbines are equipped with a thermal battery.
In the 80s, the most advanced wind turbine with a water brake of 20 m in height was built in Denmark. The reservoir with 15 tons of water occupied the lower 10 m. The thermal power of the installation was 90 kW at a wind speed of 14 m/s. The heat generator reservoir was filled with oil, t because it could be heated to a higher temperature than water. In the heat exchanger, the oil gave heat to the water
solar.lowtechmagazine.com

